Experimenting with AI models and testing different prompts is a key part of developing AI-enabled applications. However, setting up the right environment and managing model dependencies can be challenging. Podman AI Lab's Playground feature solves this by providing an intuitive, containerized environment for exploring open-source machine learning models locally. Let’s explore the Playground feature in-depth and show how it can accelerate your application development workflow when working with generative AI.
What is Podman AI Lab?
Podman AI Lab is an extension for Podman Desktop, the graphical tool for managing containers and Kubernetes, and enables developers to work with large language models (LLMs) and other AI models locally on their machine. It provides an intuitive interface to discover models, spin up playground environments for experimentation, serve models via REST APIs, and use pre-built "recipes" that showcase common AI use cases and best practices. Figure 1 shows the first screen you will see upon opening the extension.

Podman AI Lab runs the open source models in containers using Podman's container engine under the hood. This makes it easy to get started with AI without worrying about library conflicts, driver issues, or resource contention on your local machine. Since it's built on open source, you can examine how the models and example applications work under the covers (Figure 2).

Experimenting and testing AI models
Let's set up a playground environment on our local machine so we can test and compare AI models with prompts, benchmarks, and more. We’ll explore the capabilities of curated HuggingFace models, import custom models, tune performance, and integrate AI with your applications.
Setting up Podman AI Lab and downloading models
To get started, first install Podman Desktop from podman-desktop.io if you haven't already. Launch Podman Desktop, click the Extensions icon on the left sidebar, and install the Podman AI Lab extension (Figure 3).

When you open Podman AI Lab, Navigate to the Catalog, which contains a curated set of powerful open-source models that Podman AI Lab makes easy to use (see Figure 4). It includes both foundational models that can be applied to many use cases (like Mistral and Granite) as well as more specialized models for tasks like image generation and audio transcription.
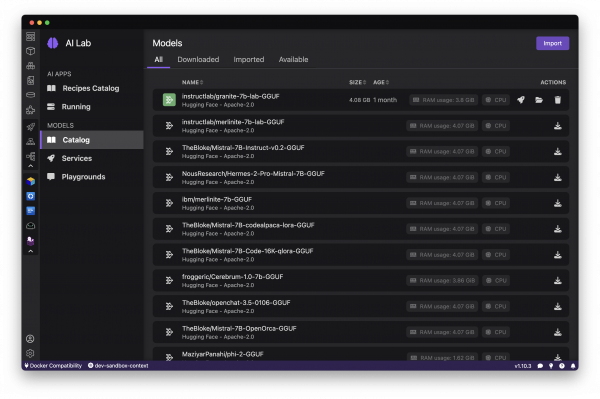
It’s also important to understand how a model can be used & redistributed, and by selecting the model itself, you can view useful details like the model provider, license, and capabilities, as shown in Figure 5.

As an example, let’s download TheBloke/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2-GGUF, based on Mistral, and while only trained with 7 billion parameters, is a well-performing reasoning model that could fit various use cases. See Figure 6.

The catalog provides many models that are already compatible with Podman AI Lab’s Recipies (sample applications to get started with chatbots, summarizers, code generation, object detection, etc.) on your local machine. You may want to consider importing your own models that you’ve discovered (perhaps from the Open LLM Leaderboard on HuggingFace) or fine-tuned using an approach like InstructLab. From the Models Catalog, you can easily import a quantized .gguf file to the catalog and make it available for use in Podman AI Lab, as shown in Figure 7.

Importing an InstructLab trained model into Podman AI Lab
Speaking of importing and working with trained models, let’s take a look at working with an InstructLab-based fine-tuned model. While LLMs are trained on immense amounts of data in a variety of subjects, the InstructLab approach allows you to fine-tune a model on knowledge and skills for specific use cases, and brings true open source to AI model development. What’s neat is that this is possible on consumer-grade hardware, and after following the instructions from the project repository, you’ll end up with a quantized .gguf file in the model-trained directory ready to use with Podman AI Lab. See Figure 8.

Experimenting with a playground environment
To interactively experiment with a model and try out different prompts, let’s launch a Playground environment. Navigate to Playgrounds from the left sidebar, where we can select New Playground and specify the name of our new environment and a downloaded model to use (Figure 9).

Podman AI Lab will spin up a containerized model server and interactive interface for sending queries and seeing results. The Playground runs the model and chat application in an isolated Podman Pod, abstracting away infrastructure complexity, and letting you easily inference the model based on the OpenAI-compatible API. See Figure 10.
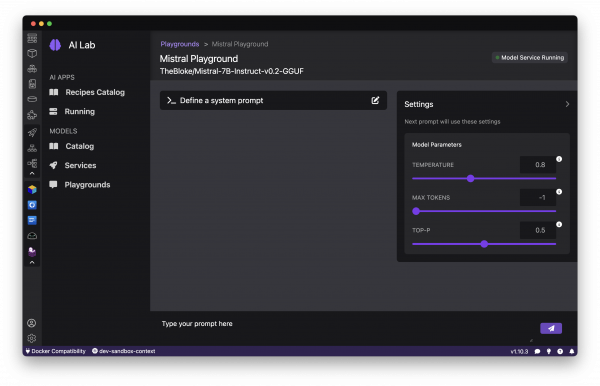
Exploring model capabilities
With a Playground launched, let’s start exploring what the model can do. Enter natural language queries or prompts and see how the model responds. Test different types of tasks, from questions to open-ended generation, to gauge the model's strengths and weaknesses, as shown in Figure 11.

You can use "system prompts" to constrain the model's behavior to align with your application's needs. For example, give the model a persona such as "You are a helpful customer support agent. Answer questions concisely and professionally." See Figure 12.

The Playground logs your conversation, so you can track what works well. Iterate to refine your prompts for accuracy, safety, and relevance.
Tuning model performance
The Playground allows you to tune the model's behavior through several configuration options, as Figure 13 depicts.
Temperature: Controls the randomness of responses. Lower values are more focused, higher values are more creative.
Max Tokens: Sets the maximum length of the model's output, influencing verbosity and resource consumption.
Top-p: Adjusts the balance between relevance and diversity in word choices.
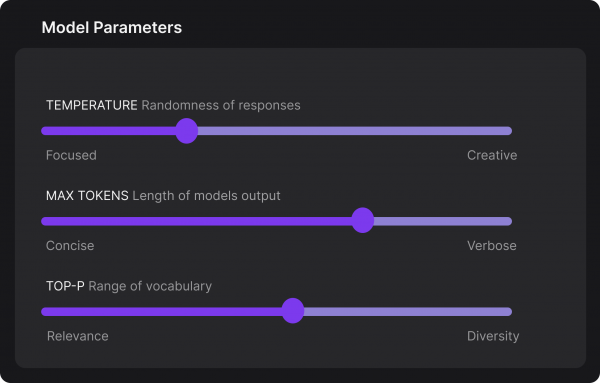
Experiment with these settings interactively to find the optimal configuration for your use case. You'll notice there are tradeoffs between predictability and creativity, as well as conciseness and comprehensiveness.
Comparing models
You can work with multiple Playground instances concurrently to compare different models on the same prompts. Evaluate the models on criteria like response quality, speed, and the size of the model. This "bake-off" can help to determine which model is the best fit for your application.
Integrating with your application
Once you've refined the model choice, prompts, and configuration, you're ready to supercharge your application with generative AI. Podman AI Lab enables you to serve the model as a containerized REST endpoint that your code can call, just like any other API. From the Services tab, select New Model Service to specify the model and port to expose (Figure 14).

The Model Serving view provides the endpoint URL along with code snippets in popular languages for making requests. Use these as a starting point to integrate the model's capabilities into your application backend. The API is compatible with the OpenAI format, so you can easily swap between local and hosted models. See Figure 15.

Let’s say we’re working on a banking application built with Quarkus, the Kubernetes-native Java stack for developer joy. We can easily integrate the generative AI model into my application by adding the new dependencies for LangChain4j and a connection to my served model to the application.properties. Now, we can create a service to interact with the LLM through a @RegisterAiService annotation, and call that method in other resources (more about Quarkus and Langchain4j here)! Figure 16 depicts this service.

Podman Desktop manages the model server container, ensuring high availability and efficient resource utilization. You can monitor its performance and logs through the Podman Desktop dashboard. Since it runs locally, you keep full control of your data and intellectual property. See Figure 17.

Conclusion
Podman AI Lab's Playground provides an intuitive, powerful environment for exploring open source AI models and testing different approaches. It abstracts away infrastructure complexity and allows you to focus on integrating AI into your applications. You can evaluate various models from the curated catalog (or import your own models), tune configurations for performance and results, and easily serve the model to an API endpoint for usage in your application, no matter the language or framework.
Try out the Podman AI Lab today, an extension of the Podman Desktop project for working with containers and Kubernetes.
Last updated: June 26, 2024