As developers, we're always looking for ways to be more productive and write higher-quality code. While tools like GitHub Copilot have gained popularity as AI pair programmers, the downside is they run on closed models and you might have to pay a subscription to use them. Imagine instead being able to use state-of-the-art free AI coding assistants right on your local machine using powerful open source models, with auto-completions and confidence that your data stays private!
Let’s take a look at how to integrate an AI code assistant into your IDE using a combination of open source tools, including Continue (an extension for VS Code and JetBrains), Ollama or InstructLab as a local model server, and the Granite family of code models to supercharge your development workflow without any cost or privacy tradeoffs. See Figure 1.
What are the Granite models?
The Granite code models, accessible here from Hugging Face, are a set of open source language models designed for AI-assisted software development. They've been trained on a variety of open source repository code spanning 116 programming languages to build a deep knowledge of syntax, semantics, design patterns, and software engineering best practices. What’s highly impressive is that the training data is all open license-permissible data through IBM's AI ethics principles for safe enterprise use and the models are released under an Apache 2.0 license.
You’ll notice that in a comprehensive evaluation on HumanEvalPack, MBPP, MBPP+, and other benchmarks, Granite consistently outperformed other open source code LLMs like Mistral-7B, LLama, and more across model scales, as shown in Figure 2.

Running models locally with Ollama
To get started running a generative AI LLM such as Granite, or any other code model, you'll first need to install a model-serving framework that can run the models on your machine. One option is with Ollama, an open source project that makes it easy to download, manage, and deploy language models on your local system (Figure 3). Ollama provides a simple command line interface for pulling models, exposing REST endpoints, and can even be deployed easily as a container.
Install Ollama on your system
After visiting the Ollama homepage, simply download the appropriate package for your operating system from the release page and run the installer. In a few clicks, you'll have the ollama command ready to use from your terminal (Figure 4).
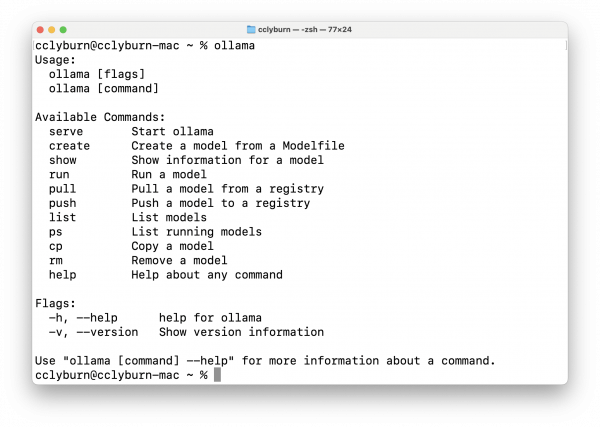
Install and serve a model with Ollama
The Ollama models library contains a curated collection of various models sourced from Hugging Face. Once you have Ollama installed, download the Granite 8B parameter model (using the latest tag will pull the 3B parameter model, and depending on your computer resources and requirements, you might want to try the 20B and 34B models) and run it with:
$ ollama run granite-code:8bSee Figure 5.

This will fetch the roughly 4.6 Gigabyte Granite 8B model and cache it locally. Ollama is now serving this model by default on localhost:11434, providing a REST endpoint and OpenAI-compatible API, and you can instantly start chatting with the model if you’d like. However, this is all you need to do to set up and start running the Granite model locally to power our AI code assistant.
Customize your model with a Modelfile (optional)
While we just demonstrated how to download and serve the Granite code model, you might want to further customize your current model, adjust custom system prompts and preferences, etc. This can be done through the Ollama Modelfile configuration to create custom setups and reuse existing models (the documentation provides information on how to do so, including working with (Q)LoRA adapters). See Figure 6.

InstructLab: An alternative model serving option
Another powerful tool for running language models locally is InstructLab (Figure 7). While Ollama focuses on getting setup quickly, InstructLab provides accessibility for developers and data scientists alike to easily fine-tune language models, both in a community workflow and to adapt models for specific use cases. Both Ollama and InstructLab use the same llama.cpp project as a backend, and work as model servers.

Install InstructLab on your system
To use InstructLab, you can install the CLI depending on your system from the repository, which involves setting up a Python virtual environment and installing InstructLab through a pip command. Once ready, you can use the ilab command to interact with InstructLab, download models, etc. (Figure 8).

Initialize InstructLab
You’ll need to briefly setup an InstructLab environment before downloading a model. As InstructLab provides a system to do model fine-tuning with a synthetic data generation process and multi-phase tuning framework, you’ll have the resources later (contained in the config.yaml and taxonomy folder) to enhance your large language model with new capabilities. Maybe you can teach it some tips and tricks about Rust!
Let’s begin by running ilab config init to set things up. Figure 9 shows the terminal window for initiating the environment.
$ ilab config init
Install and serve a model with InstructLab
With InstructLab installed and an environment setup, you can download any type of specific model from a Hugging Face repository, or an entire repository. While the default ilab model download currently pulls a pretrained merlinite model, you’ll need to first generate a Hugging Face user access token to provide to the CLI through the user settings (Figure 10).

This access token will need Read access to your account’s resources in order to pull models like Granite code, or others such as CodeLlama (Figure 11).

Be sure to save and copy the token to your clipboard, as you’ll now head back to the CLI in order to pass this along to the ilab model download command and specify a quantized version of the Granite code model from the IBM Granite Hugging Face organization (Figure 12). The command you’ll be using is the following, where you can insert your token before the InstructLab command is invoked:
$ HF_TOKEN=<YOUR HUGGINGFACE TOKEN> ilab model download --repository=ibm-granite/granite-8b-code-instruct-GGUF --filename=granite-8b-code-instruct.Q4_K_M.gguf
With the model downloaded in a models folder from your local directory, let’s serve it by running the following command (as illustrated in Figure 13):
$ ilab model serve --model-path models/granite-8b-code-instruct.Q4_K_M.gguf

Similarly, you now have an OpenAI-compatible API model server running locally, with the Granite model; however, note that the default port is 8000.
Set up the AI code assistant in your IDE
Now that you have a Granite code model running locally, it's time to integrate it into your development environment. Let’s take a look at Continue, an open source VS Code and JetBrains extension that connects your editor with language models to provide IDE-native AI assistance. Continue offers a wide set of features, including the ability to break down code sections, tab to autocomplete, refactor functions, chat with your codebase, and much more (Figure 14).

Install Continue for VS Code
To start working with Continue, first, install it from the VS Code marketplace (using Ctrl+Shift+X or Cmd+Shift+X). Search for Continue in the extensions marketplace and click Install to add the extension to your VS Code instance. You’ll now have an AI-enabled sidebar to help you through your programming tasks (see Figure 15).

Now, let’s break down how you can use either Ollama or InstructLab as model servers for the AI code assistant.
Set up the assistant with Ollama
With Ollama, first select the + icon from the bottom left-hand corner of the extension, where you can navigate through the menu to find Ollama and Autodetect the model you’re running locally. See Figure 16.

Continue should automatically detect your Ollama instance running and set up the configuration to recognize and use the Granite model. You’re good to go!
Set up the assistant with InstructLab
The setup is similar with InstructLab. After selecting the + icon, scroll a bit farther down to use the OpenAI-compatible API and, again, Autodetect for models (Figure 17).

If you need assistance with this process, you can refer to the advanced settings and set the Base URL to the appropriate address (http://localhost:11434 for Ollama or http://localhost:8000 for InstructLab) and update the advanced parameters if needed.
Verify the extension’s configuration
If you run into any trouble, be sure to check the Continue configuration file, which might already be set up with your specific model. Here, you can point to the model server, define the autocomplete model, and even setup a multi-model strategy, using the strengths of each model to help in a different capacity. Figure 18 shows a simple Ollama use case for the chat and autocomplete, but you can also add models for embeddings and reranking.

Using the open source AI code assistant
Now that you have your AI code assistant set up with Continue connected to Granite, let's dive deep into its capabilities using the Spring PetClinic sample application. This project is an excellent example of a Spring Boot application with a layered architecture, making it perfect for demonstrating various AI-assisted coding scenarios.
What can this AI code assistant do?
Let's explore the key features of our AI code assistant using specific examples from the Spring PetClinic project:
Code completions
Contextual documentation
Refactoring
Debugging
Code completions
As you type, Continue will show Granite's suggestions inline and allow you to auto-complete by pressing Tab. It can complete everything from single tokens to entire functions—for example, when finishing a method for the OwnerController class (Figure 19).

Contextual documentation
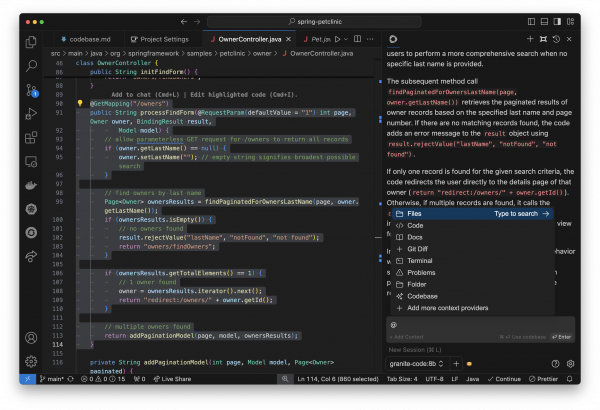
Highlight a piece of code and use cmd+L (macOS) or ctrl+L (Windows) to have Granite provide a plain-English description of what the code does, with code examples as well (Figure 20). You can ask questions about certain functions, or the codebase as a whole!

Refactoring
Select code that you want to improve and use Cmd+I (macOS) or Ctrl+I (Windows) to see Granite's suggestions. It will attempt to modernize syntax, extract methods, rename variables, and more. Accept the changes you like and iterate as needed.

Debugging
When you encounter a tricky bug, use Cmd+I (macOS) or Ctrl+I (Windows) on the problematic code section and select Debug Selection from the options. Granite will analyze the code and propose potential fixes. It can often identify logical errors, edge cases, or common pitfalls that humans might overlook. In addition, if you encounter compilation errors, this setup can help you debug the situation. See Figure 22.

Conclusion
The Granite code models, in tandem with Continue as a code assistant, and Ollama or InstructLab for model serving, provide a powerful stack for AI-assisted software development that rivals paid cloud offerings. With the efficiency of local inferencing, the comfort of data staying local on your machine, and the smooth IDE integrations, this open source setup can help you increase efficiency and reduce mundane tasks. Thanks for reading!
